Table of Content
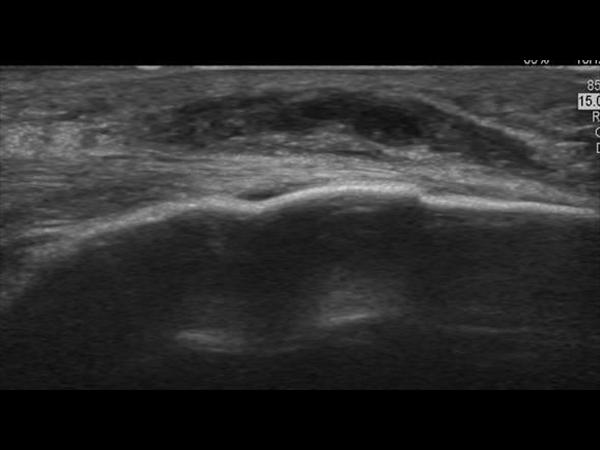
Prepatellar bursitis appears as an oval fluid-signal-intensity lesion between the subcutaneous tissue and the patella on MRI. The prepatellar bursa is located under the skin and occurs in most people. The inflammation can be of an infectious nature or a non-infectious nature. Many different aetiologies have been proposed as the cause of prepatellar bursitis. Chronic inflammation of prepatellar bursa after repetitive minor trauma is called ‘housemaid’s knee’. It can be seen in those who have to kneel very often, such as carpet layers and housemaids.

However, depending on the cause of your knee bursitis and which bursa is infected, your doctor might recommend one or more treatment approaches. There is not one “best” treatment for prepatellar bursitis. The best treatment for each individual depends on their condition and their doctor’s recommendation.
Home Remedies for Bursitis Pain and Swelling
If there is too much pressure on the bursa, it will produce more fluid to try and protect the knee and start to swell. Treatments include rest, anti-inflammatory medications, antibiotics, medications for other conditions, and surgery and other procedures if needed. Appropriate precautions to avoid trauma to the knee, avoid frequent kneeling, whenever possible, or to use protective equipment, such as bulky knee pads, for those who cannot. In the less common episodes caused by sports-related trauma, knee pads may also be beneficial in prevention. Identify and describe an appropriate history and physical examination of prepatellar bursitis. If an infection has caused the knee bursitis, your doctor will prescribe a course of antibiotic treatment.
Periodic restWhile movement and exercise are essential to overall health, cutting back on activities that irritate the bursa may reduce the chance of a flare-up. Taking periodic breaks from certain activities can also help. Since cortisone may cause tissue damage, newer treatments, including platelet-rich plasma and other regenerative medicine techniques, are sometimes used. The scientific evidence for this type of treatment is ongoing.
What causes prepatellar bursitis?
It is usually done as a day case which means that you are not admitted to hospital overnight. The knee joint can function perfectly well without this bursa and there are not usually any long-term effects to the knee. Housemaid's knee in children is more likely to be caused by infection.
Following a bursectomy or sclerotherapy, a new patellar bursa will likely develop. Prevention strategies can help ensure bursitis does not occur in this new bursa. A traditional bursectomy requires making an incision in the skin over the knee to remove the prepatellar bursa.
Who develops housemaid's knee?
Prepatellar bursitis happens when your bursa is frequently irritated, damaged or infected and makes too much fluid. The extra fluid causes your bursa to swell and puts pressure on other parts of your knee. You can usually “see” prepatellar bursitis because the front of your knee will look swollen. The role of the occupational therapist in this scenario is to address modifications of activities in patients diagnosed with prepatellar bursitis secondary to overuse. Emphasize patient education, avoidance of kneeling, and use of kneepads if kneeling is necessary. Laboratory studies are not usually indicated to diagnose prepatellar bursitis.
Customizing your diet to favor the intake of these anti-inflammatory foods can be a complementary tool in managing the symptoms of bursitis and in expediting the healing process. Moreover, it is well advised to cook with olive oil or coconut oil instead of margarine and vegetable oils in order to fight inflammation. It improves circulation and reduces swelling and stiffness. It also works as a much-needed respite for your mind and body by inducing an overall sense of relaxation.
A corticosteroid drug injected into the bursa can relieve pain and inflammation in your shoulder or hip. This treatment generally works quickly and, in many cases, one injection is all you need. Forty-eight hours after the onset of acute or chronic bursitis, warm compresses can prove to be very helpful. The application of heat stimulates blood flow to the affected joint, reduces stiffness, and fights inflammation. Furthermore, this is a useful method to prevent the accumulation of excess fluid in the affected area as well.
Osteoarthritis of the knee is a common cause of discomfort, while reactive and rheumatoid arthritis may also cause knee pain. Radiation of pain from hip fracture, osteoarthritis of the hip, slipped capital femoral epiphysis , and other disorders of the hip may refer pain to the knee. It is important to assess for cellulitis or other skin, and soft tissue infections as these can present similarly to prepatellar bursitis. Other common causes of knee pain include ligamentous and meniscal injuries within the knee joint itself. Fractures of the tibial plateau also produce discomfort within the knee. Inflammation of a bursa other than the prepatellar may produce knee discomfort.
After surgery, the knee should regain its flexibility in a few days, and you can resume normal activities in a few weeks. Your doctor will likely ask questions regarding any signs or symptoms of infection, such as fever or chills. Prepatellar bursitis caused by an infection requires a different treatment plan.
Ibuprofen commonly is used; however, alternatives are available, such as naproxen and ketoprofen. Use of a particular NSAID usually is secondary to physician and patient experience. The prognosis in prepatellar bursitis is generally good with prompt diagnosis and treatment. Hemobursa is a rare cause of acute prepatellar bursitis, except in cases of trauma or anticoagulation.
This will allow the infected fluid to drain out from the bursa. The procedure may require referral to hospital but does not normally mean an overnight stay. Generally, the function of a bursa is to help reduce friction and allow maximal range of motion around joints. When there is inflammation within a bursa , the bursa swells due to an increase in the amount of fluid within the bursa sac.
Your doctor might order blood tests or an analysis of fluid from the inflamed bursa to pinpoint the cause of your joint inflammation and pain. In case the shoulder is affected, chronic bursitis can lead to loss of motion, or a frozen shoulder, as the patient moves the shoulder less and less to avoid pain. The therapeutic benefits accorded to turmeric can be traced back to the anti-oxidant curcumin, which has shown considerable potential for healing a variety of conditions. Some studies have even shown turmeric to be helpful in the treatment of osteoarthritis.
Prevention
Generally, housemaids knee settles within a few weeks, with the correct prepatellar bursitis treatment. It is important to address any problem areas such as muscle imbalance to reduce the risk of the bursa swelling up again. Of prepatellar bursitis, both acute and chronic, can be alleviated with rest. Other remedies include anti-inflammatories, immobilization of the knee, antibiotics, medications for other conditions, and surgery. Buoy is a healthcare marketplace that connects people with the right treatment options for their situation.
Every treatment shown on this site is evaluated by our medical team and must pass Buoy's clinical review. Ask whether there is a history of a fall or acute knee injury. Fever, tachycardia or signs of systemic upset may indicate septic bursitis. Surgical drainage is required if the infection does not respond to antibiotics alone. Photos show a patient with an inflamed bursa filled with fluid in the front of her left kneecap.
No comments:
Post a Comment