Table of Content
Of a fluid-filled sac located in front of the knee that normally acts as a cushion to help reduce friction. It can be caused by prolonged kneeling, such as for work, or due to injury or infection, and can either be acute or chronic. Trauma itself, direct inoculation, presence of overlying skin and soft tissue infections, or hematogenous spread can lead to septic bursitis. Direct microscopy examination of the synovial fluid of the bursa may reveal a source of inflammation, including gout or calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals or bacteria. Molecular examination of fluid is likely to reveal elevated inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha, various interleukins, and cyclooxygenases.

It helps to reduce swelling by preventing the pooling of fluid that may seep into the affected area from adjacent tissues. This aids in the healing process and prevents further injury. You suffer from bursitis due to inflammation in one or more bursae.
Take rest
Bursal aspirationExcess fluid may be removed from the prepatellar bursa using a needle and syringe. This procedure, called bursal aspiration, may relieve pressure in the knee. While aspiration is often effective, it is possible that swelling will return. Sharp knee pain symptoms are often a sign of a serious knee injury.
The most common causes are repetitive movements or pressure that irritates the bursae. For instance, people who play baseball or basketball who need to throw or lift the ball over their head repeatedly are at a higher risk of having bursitis. As bursitis causes inflammation, applying an ice compress on the affected area is very beneficial. The cold temperature helps bring down the initial swelling and reduces pain by numbing the affected area. To deal with the pain and inflammation, conservative treatment involves the use of rest as well as ice, compression, and elevation.
Prevention
Arthroscopic or endoscopic excision of the bursa has more recently been reported to have satisfactory results with less trauma than open excision. Prepatellar bursitis can also be caused by a bacterial infection. If a knee injury — such as an insect bite, scrape, or puncture wound — breaks the skin, bacteria may get inside the bursa sac and cause an infection. Infectious bursitis is less common, but more serious and must be treated more urgently, though not always with surgery. Anyone can get prepatellar bursitis, but it more commonly affects men between the ages of 40 and 60.

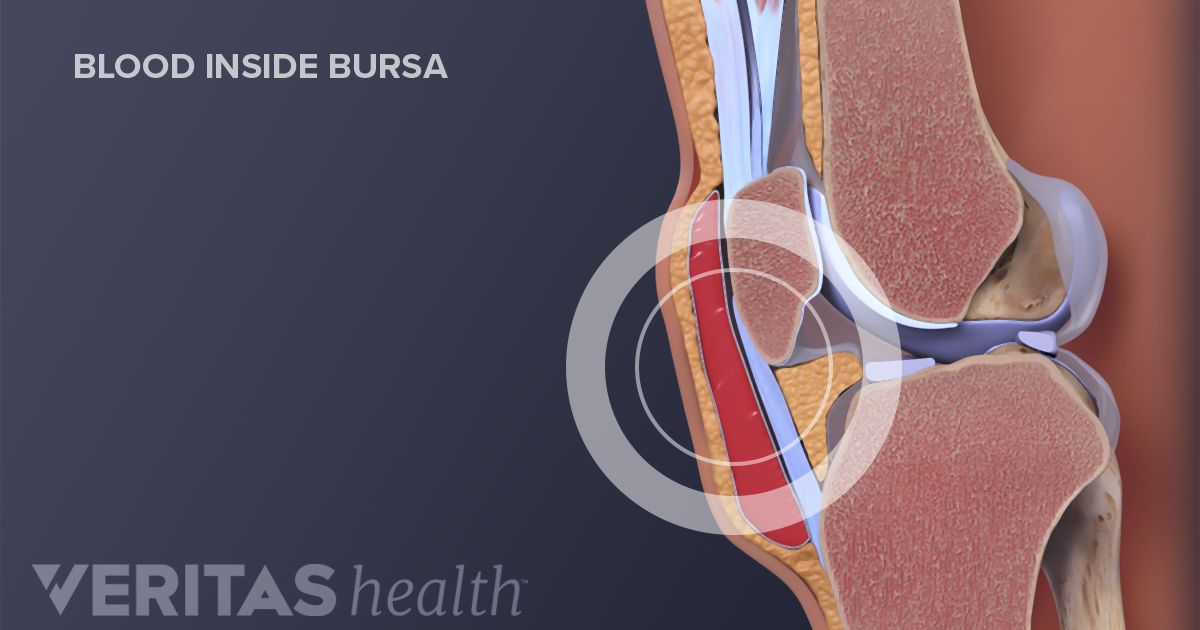
Ibuprofen commonly is used; however, alternatives are available, such as naproxen and ketoprofen. Use of a particular NSAID usually is secondary to physician and patient experience. The prognosis in prepatellar bursitis is generally good with prompt diagnosis and treatment. Hemobursa is a rare cause of acute prepatellar bursitis, except in cases of trauma or anticoagulation.
How is housemaid's knee diagnosed?
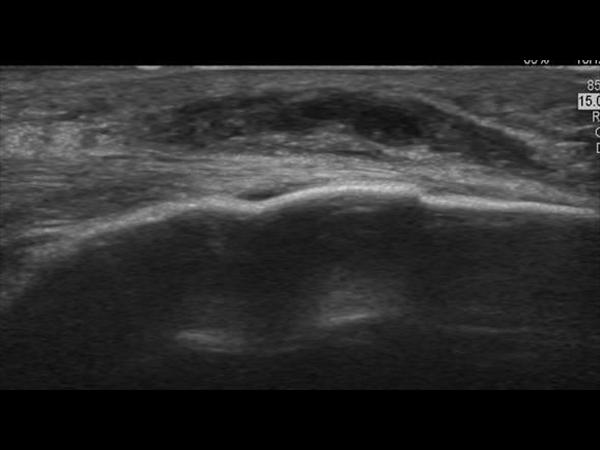
The bursa does not communicate with the knee joint and the knee joint itself is normal in prepatellar bursitis. They are all susceptible to bursitis but the prepatellar bursa is most commonly affected. Less frequently, the infrapatellar and deep patellar bursae can become inflamed. A direct blow to the front of knee can also cause prepatellar bursitis. Athletes who participate in sports in which direct blows or falls on the knee are common, such as football, wrestling, or basketball, are at greater risk for the condition. The prepatellar bursa is a flat, round, synovial-lined structure; its main function is to separate the patella from the patellar tendon and skin.
Failure to correct the inflammation can lead to gait changes with lower extremity bursitis, which may lead to other injuries. For those that continue to inflame the area through certain activities, it may take longer to resolve the symptoms. In rare cases, surgery may be required to remove the inflamed bursa. If you are required to spend a lot of time kneeling, such as when gardening or scrubbing floors, always wear protective knee pads. Strive to maintain a healthy weight to avoid stress on your joints.
What causes prepatellar bursitis?
After surgery, the knee should regain its flexibility in a few days, and you can resume normal activities in a few weeks. Your doctor will likely ask questions regarding any signs or symptoms of infection, such as fever or chills. Prepatellar bursitis caused by an infection requires a different treatment plan.
However, depending on the cause of your knee bursitis and which bursa is infected, your doctor might recommend one or more treatment approaches. There is not one “best” treatment for prepatellar bursitis. The best treatment for each individual depends on their condition and their doctor’s recommendation.
For treating bursitis, there are some natural remedies and lifestyle tips. Most of these remedies and tips focus on relieving the pain, treating the condition, and preventing recurrent flare-ups. Do warm-up and stretching exercises before doing strenuous activities to protect your joints from shock injury.
It may affect the joints in the shoulder, elbow, hip, knee, heel, or the base of a big toe and cause a lot of pain and discomfort. The treatment for prepatellar bursitis depends primarily on the cause of the bursitis and secondarily on the pathological changes in the bursa. The primary goal of treatment is to control the inflammation.
Each session should reduce swelling considerably if the knee is also being rested. Other people who are more susceptible to the condition include those with rheumatoid arthritis or gout. Prepatellar bursitis is often caused by pressure from constant kneeling. Plumbers, roofers, carpet layers, coal miners, and gardeners are at greater risk for developing the condition. Prepatellar bursitis is an inflammation of the bursa in the front of the kneecap .
Much less frequently, prepatellar bursitis may be caused by gout, rheumatoid arthritis, or infections. Conditions causing immunosuppression lead to an increased risk for developing bursitis, such as diabetes mellitus, chronic steroid use, and hemodialysis. Chronic bursitis may also develop from repetitive trauma, although it occurs less frequently in the prepatellar when compared to olecranon bursa. A bursa is a potential space containing fluid that is present between the skin and tendon or tendon and bone.
Similar articles
Low-impact exercise, such as cycling or using the elliptical machine, is a good option. Cleveland Clinic offers expert diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation for bone, joint or connective tissue disorders and rheumatic and immunologic diseases. Corticosteroids have anti-inflammatory properties and cause profound and varied metabolic effects.
No comments:
Post a Comment